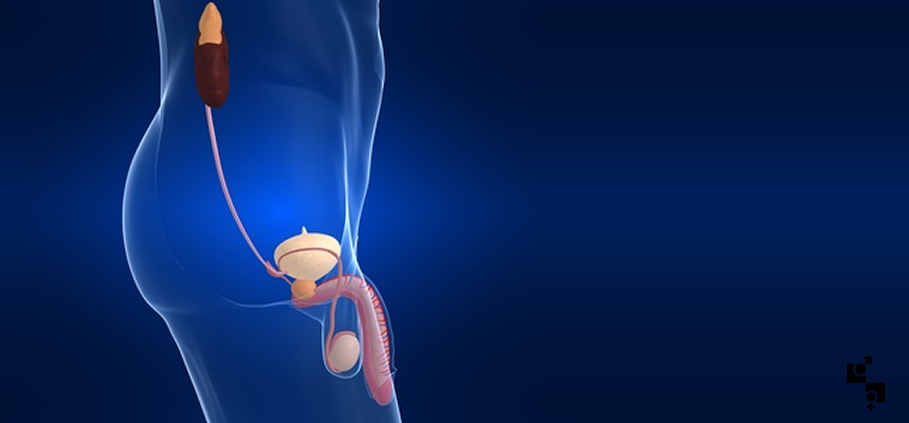
Prostate Diseases
- •Prostate Cancer video video2
- •Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- •Inflammations – Infections
- -Prostatitis
- -Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- -Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Inflammations – Infections
- -Prostatitis
With the general term “Prostatitis” we refer to the total of nosologic conditions (inflammations-infections) which share common symptoms but have different causative factors and require different treatment.
- >Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: It manifests itself with intense symptoms, fever, chills, urination disorders, pain during urination and ejaculation, blood in the urine and the sperm and pain in the pelvic area. The condition may be caused by a bacterial infection which goes through the urethra and reaches the prostate. It requires pharmaceutical treatment.
- >Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: The symptoms are milder and less severe, and include urinary disorders, blood in urine or semen, pain during urination or ejaculation, pain in the pelvic area, premature ejaculation or erectile dysfunction, and in some cases there may be no symptoms at all, in which case the diagnosis is accidental. The condition may be caused by infections of the urinary system. It requires pharmaceutical treatment.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
As Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia we define the progressive increase of the prostate size. Due to the fact that the prostate is a gland located under the male urinary bladder and surrounds the urethra, its enlargement causes problems and negatively affects the quality of life of the patient. Although the causes of BPH are not fully defined, it is certain that age and hormonal changes play a significant role in the appearance of the condition. Increased urinary frequency, need to urinate during the night, delay and difficulty in initiating morning urinary stream, prolonged urination time and urine retention are among the commonest symptoms. Depending of the size of the problem and the severity of the symptoms, the doctor will select the proper treatment, administration of medication or surgical methods for the restoration of the problem. video
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the gland. It is the second leading cause of deaths from cancer in the male population. It is usually observed in men of 60-80 years of age, has a slow development, does not metastasize and its timely diagnosis and proper treatment has positive results. Since in its earlier stages there are no symptoms, men over 45 years must undergo clinical examination and laboratory tests once a year. There are no clear causes for the appearance of prostate cancer, but major contributing factors are age, heredity, nutrition, male hormones and race. The treatment option which will be selected by the doctor depends on the progress and expansion of the disease.